Stage 3 (ACT): Embark on projects to improve and meet targets
Formulate a strategy, set targets, implement operational improvements and monitor your progress towards reducing carbon emissions.
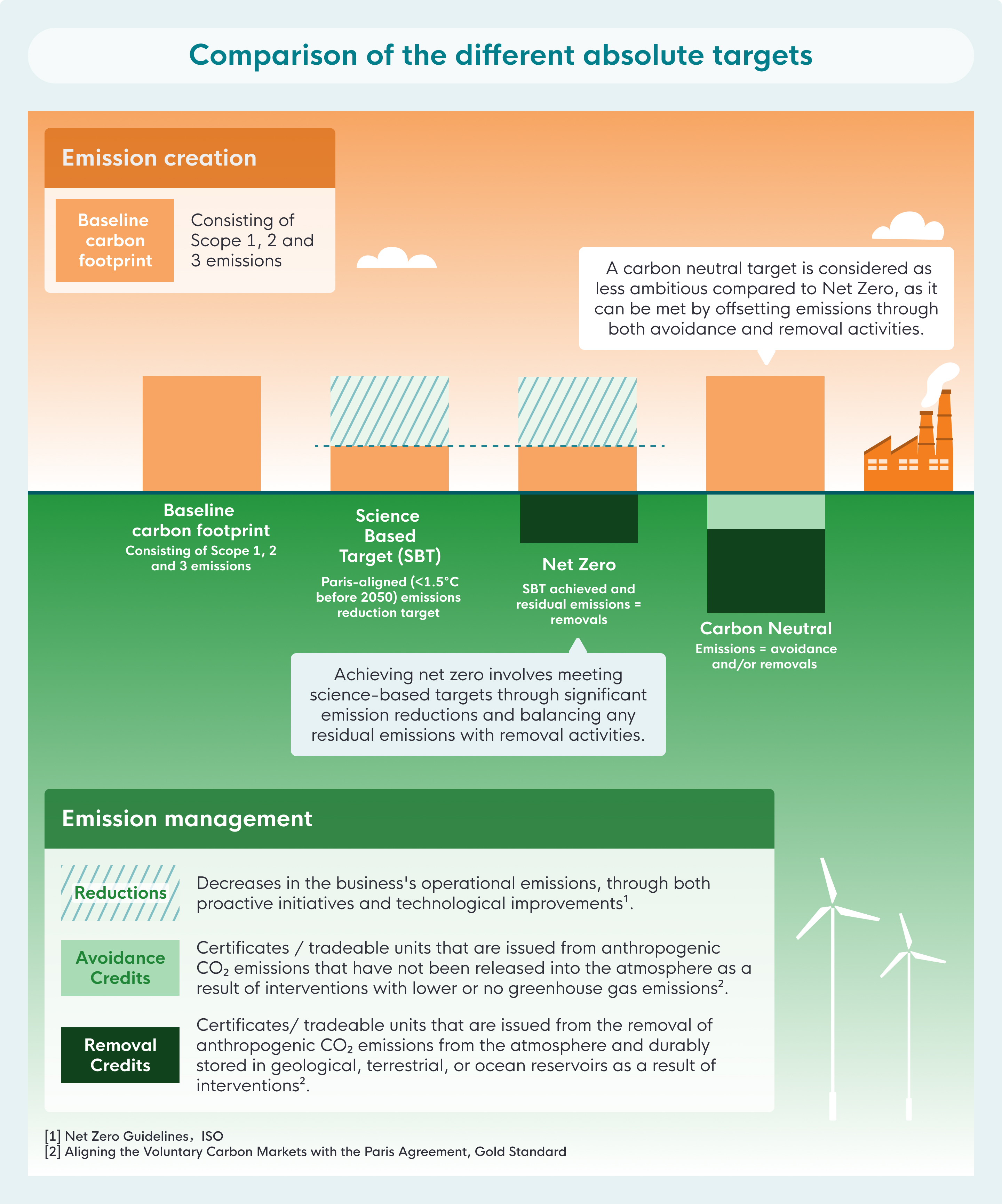
3.1 Set sustainability targets
Businesses should establish clear, achievable targets to guide long-term carbon emissions reduction efforts. Common types of targets that you can consider include:



3.2 Identify opportunities for implementation
Singapore's GHG emissions primarily stem from industrial activities and power generation. To achieve our carbon reduction goals, businesses must take decisive action through multiple approaches, including:
- Transitioning to cleaner energy sources (e.g. solar deployment)
- Making energy efficiency improvements (e.g. adopting more energy efficient equipment; process redesign; through green retail contracts)
- Optimising energy demand
For organisations with complex operations or are unclear about opportunities for improvement, an energy audit serves as an important first step. Conducted by qualified energy auditors, an energy audit examines your organisation's energy consumption patterns and efficiency levels. The audit reveals specific opportunities for energy reduction and operational improvements, providing a detailed roadmap towards reducing operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
An Energy Management System (EnMS) can also be implemented to integrate energy management into your existing business practices. An EnMS is a structured framework comprising policies, procedures and tools to provide a structured approach to energy optimisation efforts. Key components of an EnMS include:
- Energy policy
- Regular energy performance measurement
- Clear roles and responsibilities for energy management
- Documentation of energy-related processes
- Staff training and awareness programmes
- Regular management reviews
Data is essential for monitoring and improving energy performance. An Energy Management Information System (EMIS) can be installed to support the EnMS framework by automating data collection for significant energy uses. With functions for tracking, alerts and reporting, an EMIS enables efficient analysis, helping businesses to optimise energy use and achieve long-term savings.
Resources for you
NEA Energy Management & Audit Reference Manual
SS ISO 50001:2018 Energy Management Systems - Requirements with Guidance for Use
SS ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management Systems
BCA Super Low Energy Building Technology Roadmap
Implement energy efficient equipment, fittings and operational improvements
To improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions from your business operations, you can consider implementing some of the measures below. If you do not own the building or premises in which your business is located in, talk to your landlord to identify areas where emission reductions are possible, or communicate your requirements through a green lease agreement. Please note that the list provided below is not exhaustive and mandatory energy efficiency practices for large energy users in the industry sector can be found on the NEA website.
Resources for you
Grants and Programmes - Carbon Emissions and Energy Management
Energy Efficiency Grant
Sector Specific Energy Efficiency Programmes
EMA's Demand Response and Interruptible Load Programmes
Resource Efficiency Grant for Emissions (REG(E))
3.3 Monitor progress and improve performance
You should continue to evaluate and enhance the performance of your emissions reduction efforts by reviewing:
- Progress made in improving energy intensity, emissions intensity and reductions in absolute emissions
- Progress made against targets set for emissions reduction
- Identify measures that yield greater impact on emissions reduction
- Areas requiring further improvement or adjustment
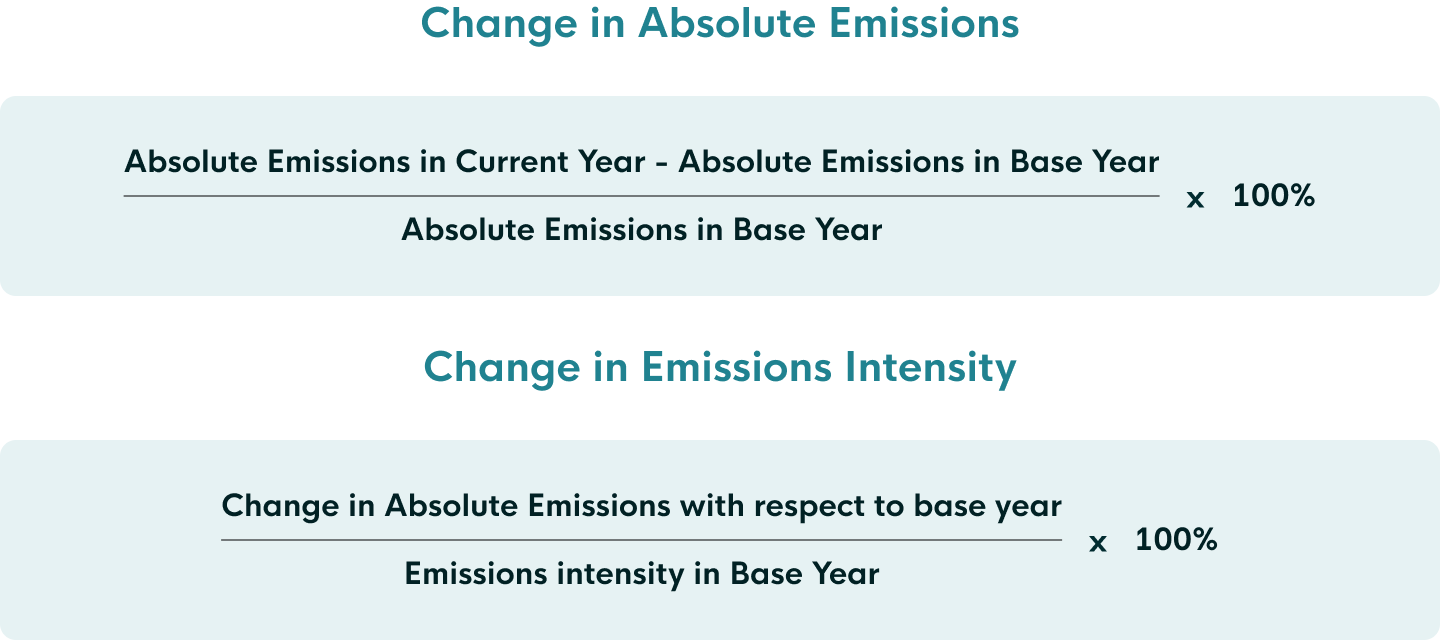
Then, regularly assess your progress against targets to determine if you're on track, exceeding, or falling short. This can be done quarterly, biannually and annually, depending on the nature of your targets. Benchmark your performance against industry norms and peers for context. Analyse data to pinpoint which measures yielded the most significant emission reductions and where improvements are needed.
Management and stakeholders should be kept informed of efforts and the progress towards targets to demonstrate your businesses' environmental commitment and achievements. For best practices in sustainability communication, explore our dedicated page on sustainability reporting.
Explore case studies of local businesses embarking on their sustainability journey: Case Studies.